Siding materials play a crucial role in defining the look, durability, and energy efficiency of your home. As the first line of defense against the elements, siding not only protects your home but also contributes significantly to its curb appeal. With a wide variety of materials available, each with its own set of advantages and characteristics, choosing the right siding can be a daunting task. In this article, we’ll explore the different types of siding materials, their benefits, and how to choose the best option for your home.
1. Understanding Siding Materials
Siding materials are the exterior cladding used to cover the walls of a building. They serve multiple purposes: protecting the structure from weather elements, providing insulation, and enhancing the aesthetic appeal of the home. Siding can be made from a variety of materials, each offering unique features in terms of appearance, maintenance, cost, and durability.
The choice of siding material impacts not only the look of your home but also its performance in terms of energy efficiency, weather resistance, and overall longevity. The right siding material can add value to your home, reduce maintenance costs, and improve its energy efficiency.
2. Common Types of Siding Materials
There are several popular siding materials, each suited to different climates, architectural styles, and homeowner preferences. Here’s a look at the most common options:
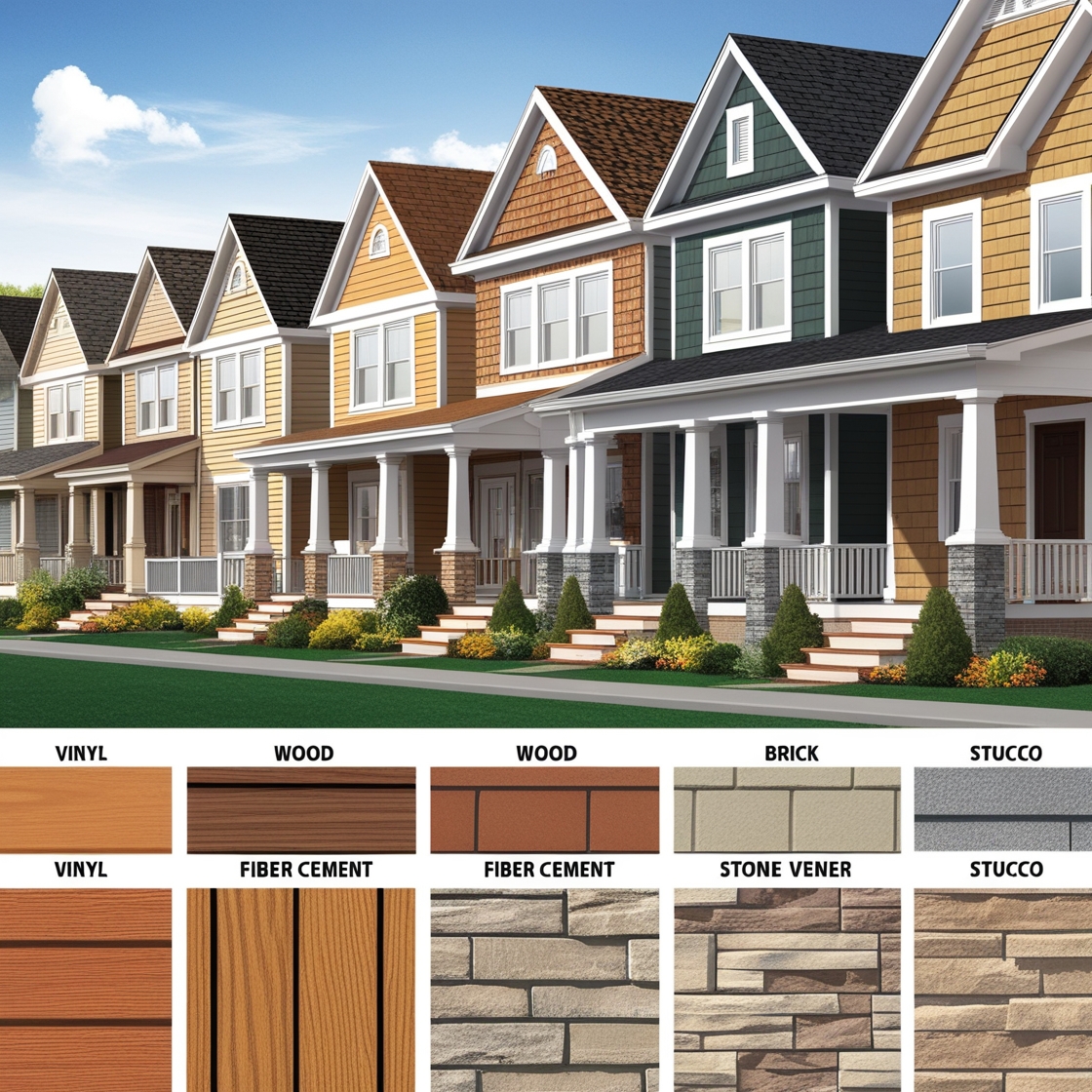
- Vinyl Siding: Vinyl siding is one of the most popular and affordable siding materials. It’s made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and is available in a wide range of colors and styles, including options that mimic wood, stone, or other materials. Vinyl is low-maintenance, resistant to moisture and pests, and never needs painting. However, it can crack or warp in extreme temperatures and may fade over time.
- Wood Siding: Wood siding offers a timeless, natural appearance that enhances the beauty of any home. It’s available in various forms, including clapboard, shingles, and shakes, and can be painted or stained in numerous colors. While wood provides excellent insulation and aesthetic appeal, it requires regular maintenance, including painting or staining, to protect it from moisture, pests, and rot. Cedar and redwood are popular choices for wood siding due to their natural resistance to decay.
- Fiber Cement Siding: Fiber cement siding is a durable, low-maintenance material made from a mixture of cement, sand, and cellulose fibers. It can be manufactured to mimic the appearance of wood, stucco, or masonry, offering versatility in design. Fiber cement is resistant to fire, insects, and rot, making it a long-lasting option. It’s also available pre-painted or primed for custom finishes. However, fiber cement is heavier and more expensive to install than some other materials.
- Aluminum Siding: Aluminum siding is a lightweight, durable material that was once a popular choice before the rise of vinyl. It’s resistant to rust, insects, and fire, and it’s recyclable, making it an eco-friendly option. Aluminum siding is available in a variety of colors and finishes, including options that resemble wood. While it’s low-maintenance, aluminum can dent easily and may fade over time, requiring occasional repainting.
- Stucco Siding: Stucco is a traditional siding material made from a mixture of cement, sand, and lime. It’s applied in multiple layers over a lath framework, creating a seamless, textured finish. Stucco is particularly popular in Mediterranean, Spanish, and Southwestern architectural styles. It’s durable, fire-resistant, and provides excellent insulation. However, stucco is susceptible to cracking in areas with shifting soil or frequent freeze-thaw cycles, and it requires proper installation and maintenance to prevent moisture infiltration.
- Brick Siding: Brick is a classic and highly durable siding material that offers a timeless appearance. Made from fired clay, brick siding is resistant to fire, insects, and weather damage, and it requires little maintenance. It provides excellent thermal mass, helping to regulate indoor temperatures. Brick siding is available in various colors and textures, allowing for a range of design options. However, it’s one of the more expensive siding materials and requires a skilled mason for installation.
- Stone Veneer Siding: Stone veneer siding is a lightweight alternative to full stone construction, offering the appearance of natural stone at a lower cost. It’s made from natural stone or manufactured materials and can be installed over existing siding. Stone veneer is available in a variety of styles, including stacked stone, ledgestone, and fieldstone, and it adds a luxurious, rustic charm to any home. While it’s durable and low-maintenance, stone veneer can be expensive and requires proper installation to prevent moisture issues.
- Engineered Wood Siding: Engineered wood siding is a man-made product composed of wood fibers, resins, and waxes, designed to mimic the appearance of natural wood. It’s available in various styles, such as lap siding, shingles, and panels. Engineered wood is more resistant to moisture, insects, and warping than natural wood, and it’s typically more affordable. It can be painted or stained, allowing for customization. However, it may not have the same longevity as natural wood or fiber cement siding.
- Steel Siding: Steel siding is a durable, low-maintenance material often used in commercial and industrial buildings but increasingly popular in residential applications. It’s resistant to fire, insects, and rot, and it can withstand extreme weather conditions. Steel siding is available in various colors and styles, including options that mimic wood or stone. It’s more expensive than vinyl or aluminum but offers superior durability. However, it can be prone to rust if the finish is damaged.
3. Factors to Consider When Choosing Siding Materials
Selecting the right siding material for your home involves considering several factors, including:
- Climate: The climate in your area plays a significant role in determining the best siding material. For example, fiber cement and brick are excellent choices for regions with extreme weather, while wood might be better suited for mild, dry climates.
- Maintenance: Consider how much maintenance you’re willing to perform. Materials like vinyl, aluminum, and fiber cement are low-maintenance, while wood and stucco require more upkeep to maintain their appearance and durability.
- Budget: Siding materials vary widely in cost. Vinyl and aluminum are generally more affordable, while brick, stone veneer, and fiber cement tend to be more expensive. Consider both the initial cost and long-term maintenance expenses when making your decision.
- Aesthetic Appeal: The appearance of your siding material should complement your home’s architectural style and your personal taste. Some materials, like wood and stone veneer, offer a natural, rustic look, while others, like vinyl and fiber cement, provide a wide range of color and texture options.
- Durability and Longevity: Consider the expected lifespan of the siding material. Materials like brick, fiber cement, and stone veneer offer long-term durability, while others, like wood, may require more frequent replacement or repair.
- Energy Efficiency: Some siding materials provide better insulation than others, helping to improve your home’s energy efficiency. Consider options like insulated vinyl or stucco, which can help reduce energy costs.
4. How to Choose the Best Siding Material for Your Home
Choosing the best siding material for your home requires a balance of aesthetics, durability, and practicality. Here are some tips to help you make the right decision:
- Evaluate Your Home’s Architecture: Consider your home’s architectural style and choose a siding material that complements its design. For example, wood siding works well with traditional and historic homes, while fiber cement or metal siding suits modern and contemporary designs.
- Consider Your Local Climate: Select a siding material that can withstand the weather conditions in your area. In coastal regions, for example, choose materials resistant to salt and moisture, such as fiber cement or vinyl.
- Think About Maintenance: If you prefer a low-maintenance option, materials like vinyl, aluminum, and fiber cement are ideal. If you’re willing to invest time in upkeep, wood or stucco may be worth considering.
- Set a Budget: Determine your budget for both the initial installation and ongoing maintenance. While some materials may have a higher upfront cost, they could save you money in the long run through lower maintenance or energy savings.
- Consult with a Professional: If you’re unsure which material is best for your home, consider consulting with a professional contractor or designer. They can provide expert advice based on your home’s needs and your personal preferences.